Business Incubator
You will learn how the unique traits of business incubators can help your business evolve. Then, you will learn step-by-step how to build your own business incubator.
In this training, you will
- Learn a brief history of business incubators.
- Compare incubators to other innovation tools.
- Learn the benefits of participating in a business incubator.
- Learn the underlying theories behind business incubators.
- Walk through how to build a business incubator.
- Explore business incubator metrics and KPIs.
Skills that will be explored
A Brief History of Incubators
The very first incubator hatched from an egg.
Amidst a robust poultry industry in the 1960s, the Rochester-based Mount Hope Hatchery was trying to meet the growing demand for poultry and was in need of 80,000 square feet to house surplus chickens. That led them to the Batavia Industrial Center close to Rochester, New York.
The Mancuso family, well-known and respected local business owners, had bought a defunct old farm machinery plant and its warehouse in Batavia, which had closed leaving thousands of local residents out of work. The family wanted to use the warehouse in some way, to help boost the local economy ideally, and planned to find tenants to lease the space. Mount Hope Hatchery’s chicken coops were some of the early businesses tenants in the space.
The idea was straightforward: lease out excess commercial space to growing businesses poorly served by existing markets. No one could foresee that the Mancuso family’s actions would become a model for diversification and innovation. As quoted in an article by Justin Peters in Wired, Mancuso family legend has it that while giving a tour of his complex in 1963, Mancuso said to reporters: “These guys are incubating chickens …. I guess we’re incubating businesses.”
Far from its humble roots, the incubator concept first seen in Batavia has since transcended regional and national boundaries to become a global phenomenon.
Incubators Compared to Other Tools
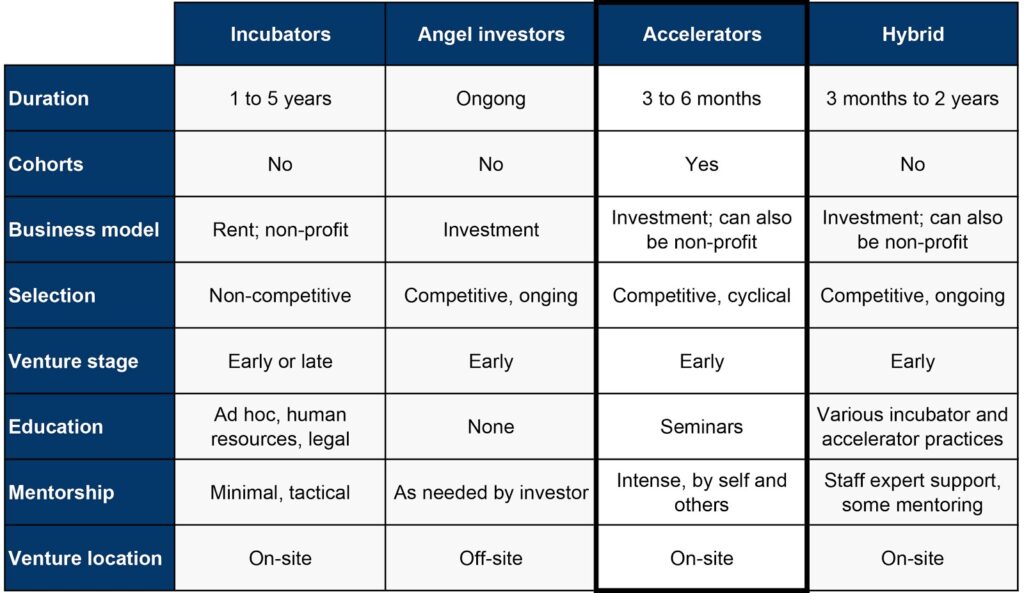
Figure 1: Comparison of startup support institutions
Image Source: Source: Cohen (2013) and Hathaway’s adaptions (2016)
Incubators share some characteristics with corporate accelerators: they interact with startups; provide physical space; and offer education programs, mentorship, and networks. But the goals and operation of these programs are much different.
Incubators operate over a longer cycle than accelerators. Startups participating in these programs tend to work on more experimental ideas and require more time to develop their product and business model. Because of these traits, the majority of incubators are non-profits, often working with local governments or universities.
This shouldn’t discourage corporates from building this tool. In the same way non-profit incubators succeed in building innovation ecosystems in local communities, corporate incubators strengthen innovation ecosystems inside companies. They also help companies commit to long-term strategy in a world focused on short-term gains.
But long-term strategies are hard to sell to leadership. Understanding the incentives for building incubators will help prospective incubator leaders secure buy-in.
Why Participate in an Incubator?
There is significant risk for companies that invest in incubators (or accelerators). There are upfront costs, and the time horizon for ROI is long. But a long-term commitment to experimentation is essential if companies are to stand a chance. Incubators can house these types of ideas.
Business incubators leverage the unique advantages and perspectives of startups, which established companies often lack. For example, Eddie Yoon and Steve Hughes explain in the Harvard Business Review that startups are better at detecting and unlocking emerging and latent market demand perhaps because they are consistently monitoring the pulse of a specific market area. Where startups often stumble, however, is when it comes to scaling their concept.
Big companies often make the mistake of creating what they can rather than what people want. They lack the agility and creativity of early-stage startups, but these big companies are more experienced at scaling. They also have advantages in logistics, such as procurement, distribution, and manufacturing, and established sales and marketing advantages.
The two entities complement each other; they can perfect a product and hold off on the scaling until the market is ready.
Large companies can benefit from and support startups’ capability to provide proof of concepts through early stage funding and later-stage M&A. But timing is everything. There are plenty of companies looking to invest in a promising startup, but there are far fewer promising startups. Yoon and Hughes explain:
“there are more buyers than sellers; if the first time an established company is made aware of a startup is by receiving a deal book from an investment banker, it’s already too late.”
Companies must stay ahead of the curve and find complimentary startups for partnerships, experimentation and acquisition.
The following list outlines some of the benefits of a corporate incubator for startups and their corporate sponsors.
Benefits for Startups
- Possible access to later venture funding
- Lower personal and financial risk
- Ready-to-use infrastructure such as office space, IT tools, and administrative business support services
- Mentorship and training, which can include individual coaching, presentation, and negotiation skills
- Assistance with business management, technology, and legal services
- The opportunity to build relationships with potential investors, suppliers, and industry experts
- If a startup is sponsored by a host company, it will likely receive funding, skills, expertise, peer support, and R&D knowledge from the host
The figure, below, summarizes the rationale for business incubators, highlighting the value derived from networks in terms of knowledge resources, access to financing, and community support.
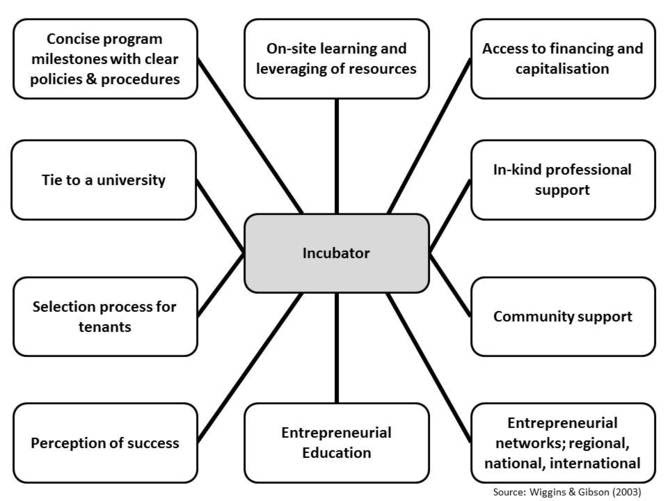
Image Source: Wiggins & Gibson, 2003
Criticisms of the Business Incubator Concept
The results of business incubators can be hard to quantify. Ernesto Tavoletti notes that in incubators “tend to fail” in supporting entrepreneurship, innovation, and regional development and are not proven policy instruments despite their popularity and the funding and promotion they receive.
Tavoletti also notes that studies that claim that incubators create jobs often originate from incubator associations and only measure the intended effects, not the unintended effects. These studies often fail to consider that firms would most likely have received funding without participating in an incubator. In some cases, studies include companies that moved into incubators later in their development to take advantage of facilities or funding.
On the other hand, a 2017 study finds that firm performance is greatly enhanced by an incubator. This study by Ayatse, Kwahar, and Iyortsuun, published in the Journal of Global Entrepreneurship Research finds that revenue growth, job creation, venture funding, networking, and alliance building all improved after the incubation process. Interestingly, the study also finds that tenants should not overstay their time in an incubation program because that could reduce their chances of survival once they graduate.
The truth here is that every incubator is different. Each requires strategic planning from people who both know the tool and know the organization. It’s important to understand the theories behind incubators, the various models, the different tenant profiles, and to hear the perspectives of incubator critics.
The Underlying Theories in Support of Incubators
In a 2012 white paper, Mathew J. Manimala and Devi Vijay of the Indian Institute of Management Bangalore presented seven theories that explain and conceptualize incubator functions.
Structural Support Theory
The structural support theory proposes that new ventures can overcome the problems associated with startups, such as being new and small, if the cost of their infrastructure and overheads can be reduced. According to this theory, “pooling resources, as occurs in an incubator context, leads to efficiencies because the central pooling of resources can significantly reduce overhead costs and thereby increase operating efficiencies.”
Structural support can include office space, communication technology, managerial assistance, access to laboratory and equipment, research facilities, and expert staff. According to this theory, the venture stands a better chance of survival if support in these areas is pooled.
Cluster Theory
The cluster theory was developed by Michael E. Porter and described in The Harvard Business Review in 1998. The theory places incubators within a broader ecosystem with other entities. Clusters are “geographic concentrations of interconnected companies and institutions in a particular field.”
The clusters are composed of industries and other linked entities important to competition. Fundamentally, they are networks and include, for example, component providers, machinery providers, services suppliers, and providers of specialized infrastructure. The advantage of being part of an incubator within a cluster is that it is easier to access resources within this environment, which increases efficiency and productivity.
According to Manimala and Vijay, the cluster theory builds on structural support theory and suggests that high-tech firms with similar characteristics in the same value chain cluster stimulate faster knowledge dissemination and synergistic growth using each other’s capabilities.
Social Network Theory
This theory posits that the effect of internal and external network connections and social networks increase the client firm’s network density and positively affect the development and growth of the startups.
“[S]ocial networks and contacts,” according to Manimala and Vijay, “facilitate access to capital, credibility and respectability because of the association with the incubator and its sponsor institutions, and they provide techno-managerial assistance through the incubator’s professionals and/or network.”
New Venture Creation Theory
With the new venture creation theory, network access and community support for entrepreneurs increases their legitimacy and the chances of venture funding and survival.
A 2004 study by Neck, Meyer, Corben, and Corbett found that incubator organizations, spin-offs, informal and formal networks, physical infrastructure, and the culture of the region where the incubator is located interact to form an ecosystem conducive to high-technology entrepreneurial activity. Additionally, the authors found greater rates of new venture formation were found following critical moments in the life of incubator organizations.
The Resource-based View
This theory states that incubators provide both tangible and intangible resources to client firms. These resources—knowledge sources in the form of universities, for example—and market proximity spur growth through a community effect. This is not unlike the cluster theory in that incubators benefit from proximity and access to networks and logistics.
Gassmen and Becker used two levels of analysis in 2006—the resource flow between the corporate incubator and the technology venture and the resource flow interface between the corporate incubator and the technology venture—to develop a model that can determine “how corporate incubators function as specialized corporate units that hatch new businesses.” They emphasize that tangible resources are all visible and easy to measure, whereas intangible resources, such as tacit knowledge and branding, are more difficult to quantify and assess.
Dyadic Theory
The concept behind this theory is that entrepreneurs “operate in an inter-dependent co-production dyad” where business assistance is provided by the sponsor. According to Hackett and Dilts (2004), incubation co-production stimulates developmental assistance in independent incubator-client dyads.
This co-development is of mutual benefit and increases the likelihood that startups survive and that the sponsor and regional economies benefit.
Real Options Theory
Real options theory borrows concepts from the finance literature. The theory states that the selection of startups or entrepreneurs for the incubator creates an option, and the injection of required resources, monitoring, and assistance are also options. The real options methodology was initially applied when evaluating technological assets such as R&D.
In 2004, Hackett and Dilts used real options theory to predict whether new ventures will survive the early stages of development. The incubator is conceptualized as an entrepreneurial firm that sources and manages the innovation process within emerging organizations. The incubator is the unit of analysis while incubation outcomes, measured in terms of startup growth and financial performance at the time of incubator exit, provide indicators of success.
Theory is one thing, but the best way to learn is by doing. The following outlines the steps to building an incubator.
How to Build an Incubator
Step 1. Select the Incubator Model
“For incubators to live up to their full economic potential, they need to overcome two pitfalls: they need to provide real value, not just office space, and they need to measure success in more than just outside funding.”
— Harvard Business Review, 2013
Internal corporate incubators
Internal corporate incubators are the most common type of incubator. They are built inside the corporation, often without walls, and the startups are often spun out when they graduate. These incubators increase the chances of intrapreneurial success, and the corporation often receives equity ownership as though they were founders of the startups.
Entrepreneurs are typically recruited to manage the startup, and internal employees may join the new company. However, not all incubated concepts are spun out, and companies use these incubators to create breakthrough products for growth and revenue. PwC states that while typical R&D seeks incremental development, incubators build company initiatives that have market viability. Incubators strive to go from concept to market.
Internal corporate incubators nearly always focus on the sectors relevant to the parent company. TechCrunch lists the following examples of successful corporate incubation programs and startup spin-outs:
- McDonalds’s spin out of Red Box (acquired by Coinstar for over $150 million)
- Google’s spin out of Niantic Labs and Pokémon GO (reportedly worth $3.5 billion)
- Oracle Labs’ development of the Java programming language
- Amazon’s Lab 126 creation of the Kindle, Echo, and Fire products
External corporate incubators
External corporate incubators provide external entrepreneurs and startups with a location, infrastructure, and resources to pursue potential ideas. Host organizations seek out startups that they believe have potential in their business area in the hopes of later financial gain and an ongoing relationship, if not an ongoing investment.
This is based on the idea of “open innovation. Originally coined by Henry Chesbrough, open innovation is the concept that companies must open themselves up to the external world for the creation and development of new products and ideas. The following table from Henry Chesbrough’s writing in MIT’s Sloan Review compares open innovation to closed innovation:

Fig 1.1
Here are some examples of open innovation provided by ideXlab:
- Audi launched the Audi Innovation Award, a contest where participants submit their concepts for the car of the future. The winner earns a $25,000 worth of consultancy.
- Procter & Gamble published a list of technical problems that their team failed to solve on the company website. Readers were asked to provide a workable solution, no matter how out-of-the-box it may have seemed.
- GE launched Ecomagination Challenge, which requests ideas from anyone who has ideas related to energy problems.
- Hewlett Packard created open innovation laboratories where researchers worldwide collaborate and create partnerships between internal teams and external scientists.
- Local Motors is a crowdsourcing startup created in 2007 by Jay Rogers, a former Marine. The model avoids the typical financial cost and time involved in designing and creating a new car because participants provide the industrial design. The winners of the design contests can also receive royalties from the car sales.
Incubators can provide the infrastructure for cooperation with the external ecosystem. The cooperation between the two entities can vary in its intensity. However, the goal is always to partner, learn, and build a successful new business that can be scaled independently either as a joint commercial venture or integrated into the host corporation.
Among external and internal incubators, there are various models and types. The U.S. Department of Commerce separates them into incubators “with walls” and “without walls.” Incubators with walls provide a separate space and location for projects, and incubators without walls (or “virtual incubators”) house the incubator within the corporate environment and use the existing infrastructure and communication systems.
Evangelos Simoudis, founder of Synapse Partners, describes the following four incubator models in his piece “Using Corporate Incubators and Accelerators To Drive Disruptive Innovation.” I suggest that a corporation should adapt these models to their needs.
The Incubator/Accelerator Model
This model includes both intrapreneurs (entrepreneurs within a corporation) and entrepreneurs. The incubation period for this type of model is typically between four to 18 months. Teams, if deemed of a high standard, are invited to join the corporation, or to “spin in.” Such teams are retained for longer with additional sponsor investment to keep them going, or they are required to work outside the corporation, as a “spin out,” with an investment from either the sponsor’s VCs or perhaps in conjunction with external VCs. Alternatively, the teams can be left to raise their own funding from external VCs or other funding sources.
This model is appropriate when a sponsoring business wants access to early stage concepts, is looking at the long term—ideally, seven to 10 years—for concept development and potential disruption, has appropriate metrics set up to measure the startup’s performance, and is open to the risks involved in mentoring and supporting an early-stage startup.
The unique benefits of this model are that there is a long-term commitment to disruption, which is crucial. Concepts need time to morph into products, time to reach the market, and time for adoption, which means that there may be some delay before there is significant ROI. Another benefit is that entrepreneurs and intrapreneurs work side-by-side and may eventually join the sponsor’s business units.
But entrepreneurs should be aware of the downsides to the model. According to Wharton Magazine, the sheer number of incubators is increasing, and not all of them are up to snuff. Some have weak investor relationships, which means that fundraising for the startups might be difficult come demo day. In addition, new programs have not had sufficient time to build a reputation or track record, which is not conducive to ready investor funding in a competitive startup market.
Wharton magazine also suggests that the time that entrepreneurs must spend at social events, building networks and discussing initiatives with potential investors, is time taken away from engineering, experimenting, and problem-solving toward a better end product.
Samsung and Telefonica are examples of firms that have applied this model.
The Pay-it-forward Model
For this model, the corporate incubator provides facilities and training while the teams work with external entrepreneurial teams. The idea is to expose teams to real-world problems in the industry and to provide resources and experts to help them solve those problems. This type of program typically lasts from six to 12 months, and the sponsoring corporation receives no equity from the startup.
This model is appropriate when the corporation wants to expose its executives to startup thinking and practices, attract entrepreneurial talent, and access new ideas and early-stage concepts from other resources to solve existing problems.
The unique benefits to corporations for this type of incubator are access to startup teams and their thinking and the creation of goodwill. A downside to this model that entrepreneurs might want to consider is that there may be a significant bias toward the interests of the corporation.
Allianz and Turner have applied this model.
The Developing Intrapreneurs Model
LinkedIn, Google, and Starbucks use this model where entrepreneurial teams incubate solutions and test business models within the organization; hence the term “intrapreneur.” This strategy works for companies that can’t pursue ideas using existing business units, so they set up a separate unit. This model fits when an organization is strongly committed to long-term concept building to achieve disruption.
The unique benefits of this model are that new products and business models can be rapidly developed. Resources are allocated to strengthen intrapreneurship and permit risk taking with out-of-the-box thinking.
One downside, according to Sean Silverthorne of Harvard Business School, is that if a startup is working on a product or service that competes in some way with the business of the company, the effort could be perceived as a threat to many inside the company.
The New Work Environments Testing Model
This model, applied by ATT Foundry and Standard Chartered Bank (SC Studio), describes creative work and the testing of new solutions or environments by the innovators.
The new work environments testing model is an incubator without walls. The sponsoring corporation does not offer on-site space for clients although they may have a central office through which to coordinate services, house the management staff, meet with clients, and perhaps even conference rooms. This is a suitable model for a corporation that wants to test startups but does not want to assume the risk of creating an external startup team.
The unique benefits to the new work environments testing model are that the corporation can use existing structures, such as flat management and open communication tools, to experiment with ideas, which reduces costs and may lead to better performance within the organization.
The New Incubator – Soft Landing for International Programs
Although a goal of incubators has been to boost local economies and ideally the national market, not all are focused on domestic markets. Many startups now use the incubator environment to reach beyond domestic boundaries.
According to the U.S. Department of Commerce, international business incubators provide the same set of entrepreneurial services as a typical incubator, but they also provide a “soft landing” for international firms seeking to enter the U.S. market.
These types of incubators often provide specialized services. For example, the University of Florida’s soft landing program helps both domestic and international firms integrate into the Central Florida business community. The program helps with short-term leased office space, networking with the Central Florida business community, domestic market research, and provides access to experts on legal, government, regulatory, and press and media matters.
The University of Toronto has partnered with the Chinese firm Diantou.net to help companies who are entering the lucrative Chinese market. According to The Impact Centre at the University of Toronto center, Diantou.net will “provide start-ups with legal, marketing and other support services” while the Toronto center will offer entrepreneurship courses to Chinese students, researchers, and startups.
Other similar incubators offer translation services, language training, assistance with documentation such as obtaining business and driver’s licenses, cultural training, assistance with visa and immigration, and housing assistance.
Consider these examples and design a model that best suits your organization and its goals.
Step 2. Select Your Industry Focus
Most incubators are focused on a specific industry such as digital education, green technology, homeland security, fashion, or food. An industry focus ensures that the available skills and resources are optimized and targeted.
Technology incubators are specifically focused on emerging technologies such as software, biotechnology, robotics, or instrumentation. A service incubation program, as the name implies, focuses on entrepreneurial firms in the service sector, for example, landscapers, graphic designers, accountants, and internet-based companies. However, mixed-use incubators, or general-purpose incubators, nurture the growth of all types of companies and may not fit into any specialized niche.
According to Nola Hewitt-Dundas, incubators are increasingly oriented toward knowledge-intensive activities such as knowledge dispersion among collaborating actors and a more open collaborative model. While customers and suppliers have traditionally been valuable contributors to incubator projects, universities are now also increasingly involved.
Step 3. Select Your Program Length
While corporate accelerators generally stick to a 3-month program, corporate incubators don’t have a strict duration. According to Accion, many incubators require a one- to two-year time commitment that includes incubator training and workshops. At the Polytechnic Institute at New York University, entrepreneur teams typically spend 18 months in the program while other incubators take much longer.
The SPARK Regional Incubator Network in Ann Arbor is structured so that companies graduate from the incubator in two to three years. Clients initially commit to a standard one-year lease. If the business meets their desired milestones, the lease is renewable for one or two additional one-year leases.
The duration of internal incubators depends on how long the company expects the concept to take to see quantifiable value, according to Robert Wolcott of Kellogg Insight. But that’s the tricky part when it comes to early stage concepts. Wolcott explains that a startup may not see any returns for four or five years. Therefore, to retain the commitment of a host corporation, startups must demonstrate some other quantifiable value. Wolcott estimates that this must be achieved within 18 months to keep a corporate board happy.
The reason for this “need to produce” is the budget cycle. According to Wolcott, not much is expected of an incubator startup in the first three or four months. But, after a year, financiers are itching for positive indicators. With no results to speak of after 18 months, a startup might have a target on its back if it doesn’t come up with some proof of positive impacts.
Step 4. Select Your Location
Location considerations are similar to those of corporate accelerators.
Brad Feld, co-founder of Techstars, suggests that business incubators can thrive in any location. His opinion is that because many incubators are “virtual” and lack walls, incubators do not have to be in the same geographic area as the host organization. Rather, it might be better for the incubator to be located where there is optimal access to knowledge and physical resources. Close to a university, for example.
In the case of tech startups, and in the case of Silicon Valley, tech incubators benefit from the networks and events in the local area. According to Michael Seibel of Y Combinator, the Valley offers “money and good valuations. We can introduce them to tons of other companies that can be mentors and customers, and we can introduce them to the pace of the Valley … We can’t do that anywhere else.”
According to the U.S. Department of Commerce, graduating entrepreneurs tend to stay in the same geographic region as their incubator organizations and, in most technical industries at least, entrepreneurs usually start businesses related to their previous work. Thus, because most entrepreneurs do not move to start a business, the possibilities for high-technology startups may be limited in some locations.
Where virtual incubators are concerned, they may be able to build a thriving ecosystem of their own, remote from the host organization—particularly if the location provides valuable external networks and resources.
Visual Representation of a Virtual Business Incubator
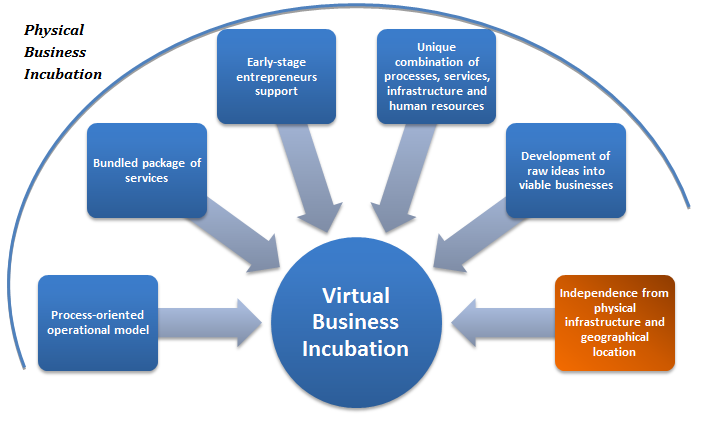
Image Source: World Business Incubation, 2015
Image Source: World Business Incubation, 2015
Step 5. Select Your Learning Program
Business incubators and accelerators are fundamentally engines for learning. But the type of learning that you require, as well as the knowledge and skills that each startup team requires, will differ. A diagnostic process can help you to determine how best to allocate resources for learning so that both entities are served.
A model developed by Campbell, Kendrick, and Samuelson shows four basic areas or “services” where incubators contribute – revenue growth, employment or job creation, venture funding, networking, and alliance-building. The value addition activities begin with a diagnosis of needs, which is applied to prospective incubatee’s new business proposals. Once this diagnosis is complete, you can tailor the learning experience for participating startups. For more on learning programs, see our piece in corporate accelerator design.
Step 6. Select Your Tenant
Just as there are different incubator types and models, there are also different types of tenants who may or may not be viable participants in one or more of the incubator models. A lot depends on the support and the resources that you, the host company, are willing or able to provide and whether the startup is in the same industry vertical as the sponsor.
When seeking a tenant, consider their maturity and readiness. Ernesto Tavoletti describes four types of incubator tenants.
- Anchor tenants are typically mature entrepreneurs and can contribute financially to the incubator. They do not require input from the corporate host. Examples of this type of tenant include accounting companies, law and financial services firms, economic development agencies, or university offices.
- Long shots are early-stage startups that require a nurturing environment from the corporate host. These entrepreneurs are aware that they lack resources and require co-production efforts from their host to reach their potential.
- Up-and-comers also have significant resource gaps that can be addressed through co-production. These companies are one step ahead of long shots in terms of maturity and are operated by entrepreneurs who are aware of the gaps but are on the verge of being able to engage with resource assistance.
- Superstars have matured beyond the up-and-coming stage, and they are ready to engage with minimal co-production efforts from the host. They have resolved problems, can withstand crises, and expect to imminently graduate from the incubator. These companies can act as role models for up-and-comers and long shots.
Step 7. Manage Your Incubator
Given the long-term nature of incubators, they require strategic management.
The U.S. Department of Commerce found that successful incubators have adopted certain practices such as crafting a written mission statement, selecting clients based on cultural fit, their potential for success, reviewing client needs at the entry stage, showcasing clients to the community and potential funders, and charging for rents and service fees.
These factors all stem from successful incubator leadership.
Incubator Leadership
When first creating an incubator, it’s crucial to identify and hire a strong entrepreneurial leader. According to a white paper by the Aspen Institute and National Entrepreneurship Network of India, cost concerns could derail the incubator at the outset if they inhibit hiring someone of the right caliber.
To give some idea of leadership experience, according to the U.S. Department of Commerce, on average, incubator managers have 8.1 years of experience in the business incubation industry including 7.5 years at their current position. Over 50 percent of the time of these managers’ is spent delivering client services, building internal and external networks for the program, and facility management.
A study by Monsson and Berg (2016) found that incubation managers had a moderately positive influence on incubators in terms of facilitating access to important actors, assisting with practical advice, and the daily management of the incubator program. According to the authors, the “modest role” played by managers reflects a preoccupation with operational tasks rather than a greater role creating partnerships and synergies.
Financial Commitment and Risk
Incubators and accelerators are a financial commitment. In addition to private funding and investors, public funding of incubators is common.
In Canada, for example, governments provide funding for incubators. However, in Canada,, Sunil Sharma, the chair of the board of the Canadian Acceleration and Business Incubation Association, expressed to The Globe and Mail the concern that there’s already too much government money going to programs that support tech startups.
According to Sharma, “It’s time to really take stock of how much funding has been put into supporting entrepreneurs in Canada and really measure it against the outcomes that we should have been able to show by now.”
According to the U.S. Department of Commerce, there is a significant correlation between the size of a business incubation program’s budget and program success; that is, the bigger the budget, the greater the success. However, it is also important to look at revenue sources and how the incubator uses its resources. This research found that receiving a large portion of revenues from client rent and service fees is positively correlated with outcome measures, although the effect is only statistically significant for three client firm outcomes. On the expenditure side, the more programs invest in staffing and program delivery—relative to building maintenance or debt servicing—the higher the probability of improved client firm outcomes.
Incubation program budgets range from revenues of $33,000 with expenses of $17,000 to $2.8 million in revenue with expenses of $2.5 million, according to the U.S. Department of Commerce, but data is scarce on this subject. The lack of quantitative data on the value of incubators emphasizes that the risks should be carefully weighed against the potential gains.
Step 8. Conduct a Post-Program Assessment
The success of incubators and accelerators depends on how the program is managed after startups graduate. Networks and relationships make or break these programs. Successful startups give back to the program, and startups succeed partly because of continued contact from incubator hosts. See our piece on post-program strategies for corporate accelerators for more.
Measuring Incubator Success
“In addition, the business models of many for-profit dot-coms failed to consider that, on average, it takes slightly more than three years to successfully incubate a client firm—and perhaps up to six years or more for that firm to realize significant growth. However, interviews with former managers of dot-com programs suggest that their business plans speculated that clients would begin to turn a profit in 12 to 18 months—or even as few as six months. This flaw in the model most likely contributed to the rapid decline of the dot-com incubator.”
— US Department of Commerce, 2011
Incubators have similar timeframes with corporate accelerators. While working with startups may imply faster growth, both accelerators and incubators start to create true value after they’ve had time to develop, generally within four to seven years. Incubators, in particular, are harder to quantify during their early stages. Compared to accelerators, the lack of time constraints and PR efforts limit short-term results. (We dive deeper into the time frame for these tools in our article on corporate accelerator management.)
Combine this reality with the risks involved, and it can be difficult to get buy-in from the board. Corporate decisions are based on an annual schedule while, according to Dave McClure of 500 Startups, startups live and die within that period.
To secure buy-in, incubator leaders must think critically to align the implicit benefits of incubators with business goals.
Incubator Metrics and Kpis
The research is mixed when it comes to measuring the success of incubators, much of it claiming that past metrics and performance are either impossible to measure, or the studies suggest using varying metrics. The table below highlights some of the literature findings.
As evidenced by the past incubator studies, these tools are often studied through a policy lens. This is because the majority of incubators are non-profits. While building local entrepreneurial ecosystems is good for the company in the long term, it’s not the best metric for selling these tools to corporate leadership.
Ayatse, Kwahar, and Iyortsuun’s 2017 review of existing incubator literature found that there is no objective performance measure that can be applied across business incubators. Instead, firms and researchers must make up their own. Metrics identified during their research were the following:
- revenues
- finance
- venture capital funds
- graduation from incubation program
- firm survival
- networking activity
- innovative firms
- organizational or firm growth
- job creation
- sales growth
- profitability
- patents registered
- number of patents application
- alliance
- technology transfer
- employment growth
- technology growth or development
- research and development productivity
- ability to share knowledge and technology
- high-tech employment.
The above bullet points can give incubator leaders some ideas for KPIs, but it is up to the individual organization to decide how to best serve business goals. For more on balancing business goals with startup engagement programs, see our article on corporate accelerator management.
What Does Success Look Like for Corporate Incubator?
According to EY, studies show that approximately 90 percent of a company’s development efforts never result in commercialized products or services. This could imply that a successful incubator is nothing more than a random incident because there are few defined consistent metrics with which to measure or benchmark incubators.
Bakkali, Messeghem, and Sammut suggest the balanced scorecard, developed by the Harvard Business School, as a particularly useful tool to measure the success of incubators.
The balanced scorecard approach first determines what overall success of the company looks like (ROI, reputation for excellence, growth in market share, etc.) and derives measurable activities that reflect these goals. The activities are categorized by strategic focus, as seen in the diagram below.
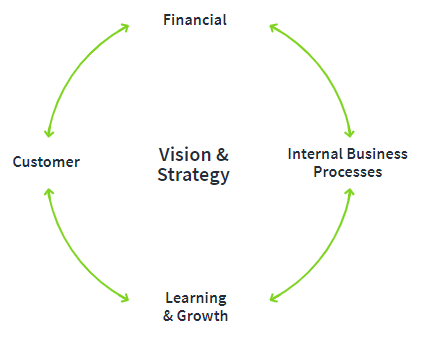
Image Source: QuickScore, 2020
Bakkali, Messeghem, and Sammut (2013) explain that incubator managers insist on risk reduction because they focus excessively on short-term economic indicators. According to the authors, the balanced scorecard is fundamental to the learning process regarding incubator impacts.
What Does Success Look Like for the Startup?
Incubators are proven to be beneficial for participating startups. For instance, Eric Harwit, a Fulbright fellow, published a report in 2002 that found that 87 percent of firms that graduated from an incubator were still in business.
Hackett and Dilts (2004) offer more concrete metrics and define the outcome of the incubation process according to five mutually exclusive outcome states that are measured in terms of growth and financial performance at the time of incubatee graduation. These outcome states are the following:
- The incubatee is surviving and growing profitably.
- The incubatee is surviving and growing and is on a path toward profitability.
- The incubatee is surviving but is not growing, not profitable, or is only marginally profitable.
- Incubatee operations were terminated while still in the incubator, but losses were minimized.
- Incubatee operations were terminated while still in the incubator, and the losses were large.
A white paper by the Aspen Institute and National Entrepreneurship Network of India (2013) provides in-depth information on the problems of measuring incubatee success. The paper discusses exit factors as metrics but emphasizes that what might be a successful exit for one incubator will be different for another. A high-growth technology start-up may consider raising a certain amount of capital as a successful factor for exit, whereas a medium growth start-up may consider positive cash flow and profits a successful factor for exit.
For this metric, the incubator would need to define its successful exit factors based on the type of start-ups that it would incubate. Other suggested exit factors are the following:
- During a one to three-year incubation period—customers/user base, capital raised, product launched, valuation, revenue, jobs
- At graduation after a one to three-year incubation period—revenue growth, valuations, jobs, total capital raised, social impact
What Does Success Look Like for Non-profit Incubators?
The goal of a non-profit incubator is to set up a robust entity that can sustain the creation of value in a local economy. Possible metrics include ongoing impact in the form of new entrepreneurs created, jobs created, and revenue to fuel local economies. According to the Aspen Institute and National Entrepreneurship Network of India (2013) white paper, however, these developments typically take between four to five years to mature and require a ifferent focus, resources, and outcomes along the way as the incubator progresses.
Over the long term, revenue and jobs are goals of an incubator but, according to the white paper, they may also be useful as active indicators to determine the immediate success of the startup.
Ultimately, tracking jobs, revenue, return on investment, and societal impact over a period of four to six years is ideal for measuring impact. This would include the period of incubation (1.5 to three years) and post-incubation (one to three years).
When comparing incubators, additional exogenous factors to consider are geographic location and the local economy—for example, the value of a company and the jobs it creates in a tier 1 town versus a tier 2 town—and the impact on the lives of the people in the community. The impact of a company in terms of education, livelihoods, and life expectancy might differ greatly depending on the location.
The Aspen Institute and National Entrepreneurship Network of India (2013) white paper outlines key challenges that incubators face to become successful—decision implications for partners, funders, and policymakers. Successfully implementing the right metrics and milestones would enable higher motivation, strong incentives, and the propagation of best practice knowledge for greater success of incubators as an industry.
However, classifying incubators and analyzing their metrics helps highlight some key challenges that must both be recognized and dealt with to ensure a higher chance of success.





